ARIC EA hg38 validation
::: {.container-fluid .main-container} ::: {#header .fluid-row} # psychencode_hg38_validation {#psychencode_hg38_validation .title .toc-ignore}
2020-12-22
:::
workflowr
::: tab-content ::: {#summary .tab-pane .fade .in .active} Last updated: 2021-09-08
Checks: 5 2
Knit directory: ~/Github/ARIC/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.2). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
The R Markdown is untracked by Git. To know which version of the R Markdown file created these results, you’ll want to first commit it to the Git repo. If you’re still working on the analysis, you can ignore this warning. When you’re finished, you can run wflow_publish to commit the R Markdown file and build the HTML.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(12345) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Using absolute paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it difficult for you and others to run your code on a different machine. Change the absolute path(s) below to the suggested relative path(s) to make your code more reproducible.
| absolute | relative |
|---|---|
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/test_data/GWAS | test_data/GWAS |
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/results/SPrediXcan | results/SPrediXcan |
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/models | models |
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/code | code |
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Untracked files:
Untracked: .DS_Store
Untracked: .Rhistory
Untracked: ARIC_EA_hg38_validation.Rmd
Untracked: ARIC_EA_hg38_validation_height.Rmd
Untracked: ARIC_EA_hg38_validation_height.html
Untracked: PWAS/
Untracked: code/
Untracked: covariances_EA_hg38.Rmd
Untracked: figure/
Untracked: models/
Untracked: results/
Untracked: test_data/
Untracked: weights_EA.Rmd
Untracked: weights_EA.htmlNote that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
There are no past versions. Publish this analysis with wflow_publish() to start tracking its development.
| ::: |
|---|
| title: ARIC EA hg38 validation author: Sabrina Mi date: ‘2021-09-08’ |
psychencode_hg38_validation
2020-12-22
workflowr
Last updated: 2021-09-08
Checks: 5 2
Knit directory: ~/Github/ARIC/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.2). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
The R Markdown is untracked by Git. To know which version of the R Markdown file created these results, you’ll want to first commit it to the Git repo. If you’re still working on the analysis, you can ignore this warning. When you’re finished, you can run wflow_publish to commit the R Markdown file and build the HTML.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(12345) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Using absolute paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it difficult for you and others to run your code on a different machine. Change the absolute path(s) below to the suggested relative path(s) to make your code more reproducible.
| absolute | relative |
|---|---|
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/test_data/GWAS | test_data/GWAS |
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/results/SPrediXcan | results/SPrediXcan |
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/models | models |
| /Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/code | code |
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Untracked files:
Untracked: .DS_Store
Untracked: .Rhistory
Untracked: ARIC_EA_hg38_validation.Rmd
Untracked: ARIC_EA_hg38_validation_height.Rmd
Untracked: ARIC_EA_hg38_validation_height.html
Untracked: PWAS/
Untracked: code/
Untracked: covariances_EA_hg38.Rmd
Untracked: figure/
Untracked: models/
Untracked: results/
Untracked: test_data/
Untracked: weights_EA.Rmd
Untracked: weights_EA.htmlNote that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
There are no past versions. Publish this analysis with wflow_publish() to start tracking its development.
Liftover
Definitions
conda activate imlabtools
METAXCAN=/Users/sabrinami/Github/MetaXcan/software
DATA=/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/test_data/GWAS
RESULTS=/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/results/SPrediXcan
MODEL=/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/modelsValidation
Definitions
.
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(tidyverse))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(qqman))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(data.table))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(RSQLite))DATA="/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/test_data/GWAS"
RESULTS="/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/results/SPrediXcan"
MODEL="/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/models"
CODE="/Users/sabrinami/Github/ARIC/code"
source(glue::glue("{CODE}/load_data_functions.R"))
source(glue::glue("{CODE}/plotting_utils_functions.R"))
gencode_df = load_gencode_df()Run S-PrediXcan
Run S-PrediXcan with the ARIC model.
python $METAXCAN/SPrediXcan.py \
--gwas_file $DATA/imputed_CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.txt.gz \
--snp_column panel_variant_id --effect_allele_column effect_allele --non_effect_allele_column non_effect_allele --zscore_column zscore \
--model_db_path $MODEL/ARIC_EA_hg38.db \
--covariance $MODEL/ARIC_EA_hg38.txt.gz \
--keep_non_rsid --additional_output --model_db_snp_key varID \
--throw \
--output_file $RESULTS/CAD_ARIC_hg38.csvAnd the mashr model.
python $METAXCAN/SPrediXcan.py \
--gwas_file $DATA/imputed_CARDIoGRAM_C4D_CAD_ADDITIVE.txt.gz \
--snp_column panel_variant_id --effect_allele_column effect_allele --non_effect_allele_column non_effect_allele --zscore_column zscore \
--model_db_path $MODEL/mashr_Whole_Blood.db \
--covariance $MODEL/mashr_Whole_Blood.txt.gz \
--keep_non_rsid --additional_output --model_db_snp_key varID \
--throw \
--output_file $RESULTS/CAD_mashr_Whole_Blood.csvCompare Association Results
spredixcan_association_ARIC = load_spredixcan_association(glue::glue("{RESULTS}/CAD_ARIC_hg38.csv"), gencode_df)
dim(spredixcan_association_ARIC)[1] 1318 16significant_genes_ARIC <- spredixcan_association_ARIC %>% filter(pvalue < 0.05/nrow(spredixcan_association_ARIC)) %>% arrange(pvalue)spredixcan_association_Whole_Blood = load_spredixcan_association(glue::glue("{RESULTS}/CAD_mashr_Whole_Blood.csv"), gencode_df)
dim(spredixcan_association_Whole_Blood)[1] 12587 16significant_genes_Whole_Blood <- spredixcan_association_Whole_Blood %>% filter(pvalue < 0.05/nrow(spredixcan_association_Whole_Blood)) %>% arrange(pvalue)Then compare ARIC and Whole Blood z-scores.
zscores = inner_join(spredixcan_association_Whole_Blood, spredixcan_association_ARIC, by=c("gene"))
dim(zscores)[1] 815 31zscores %>% ggplot(aes(zscore.x, zscore.y)) + geom_point() + ggtitle("S-PrediXcan z-score") + xlab("mashr Whole Blood") + ylab("ARIC") + geom_abline(intercept = 0, slope = 1)Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).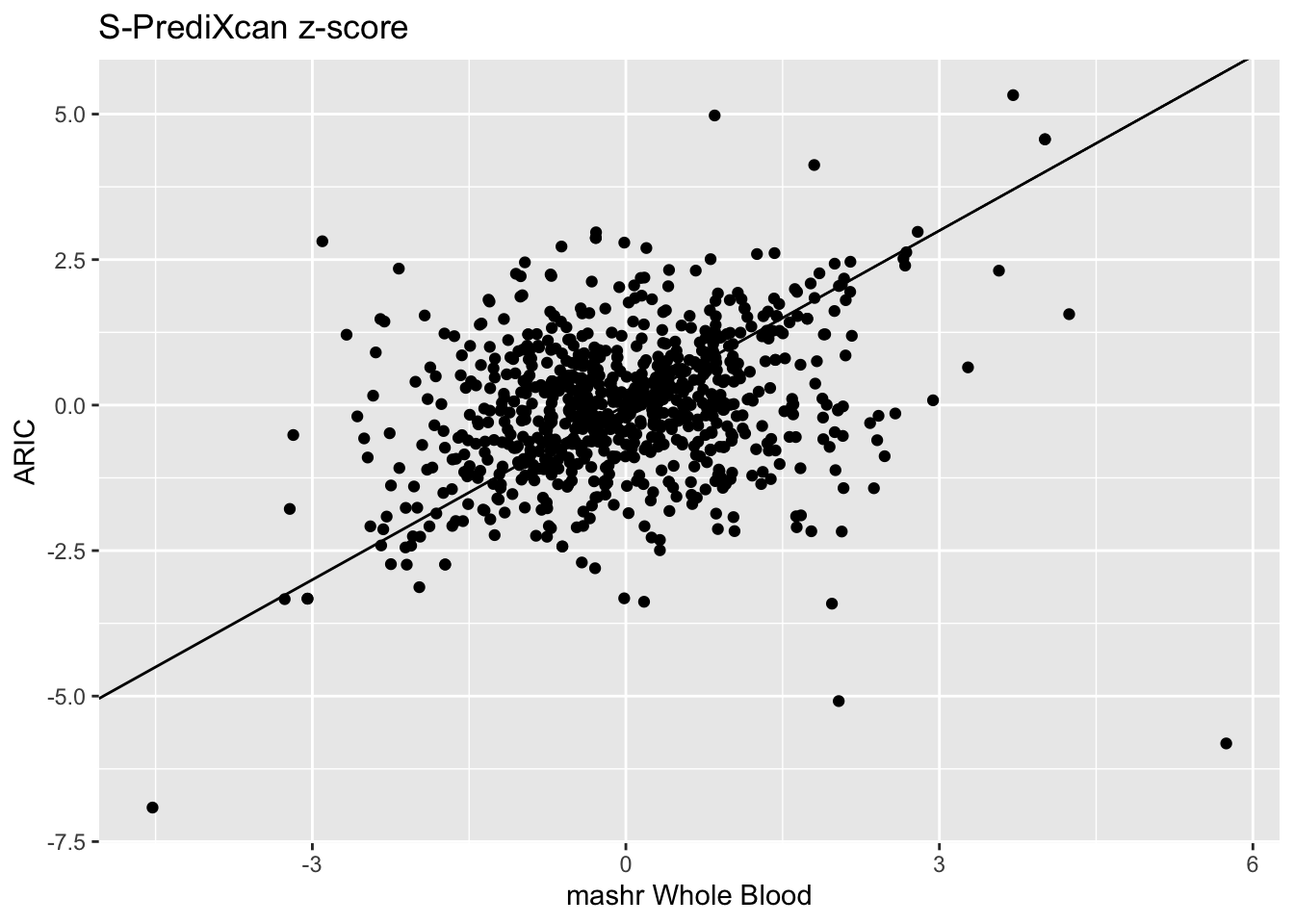
We can compare the significant genes found with the ARIC and mashr Whole Blood models.
significant_genes_ARIC[, c(1,2)] gene zscore
1 ENSG00000186063 -6.914873
2 ENSG00000160712 -5.813218
3 ENSG00000169174 5.326004
4 ENSG00000133789 -5.085480
5 ENSG00000107562 4.976651
6 ENSG00000158710 4.567579
7 ENSG00000158710 4.567579
8 ENSG00000175573 4.125269significant_genes_Whole_Blood[, c(1,2)] gene zscore
1 ENSG00000134222 -9.263287
2 ENSG00000107798 7.525837
3 ENSG00000163596 7.210367
4 ENSG00000138380 -5.982736
5 ENSG00000160712 5.744854
6 ENSG00000127616 5.703439
7 ENSG00000183431 -5.382606
8 ENSG00000182511 -5.373519
9 ENSG00000115486 5.258467
10 ENSG00000084093 -5.204898
11 ENSG00000143498 4.920139
12 ENSG00000031698 -4.747462
13 ENSG00000168906 -4.698991
14 ENSG00000130475 -4.683521
15 ENSG00000119718 4.681344intersect(significant_genes_ARIC$gene,significant_genes_Whole_Blood$gene)[1] "ENSG00000160712"There is only one gene found significant in both, ENSG00000160712
Session information
sessionInfo()R version 4.0.3 (2020-10-10)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin17.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Big Sur 10.16
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.0/Resources/lib/libRblas.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.0/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] RSQLite_2.2.1 data.table_1.13.2 qqman_0.1.4 forcats_0.5.0
[5] stringr_1.4.0 dplyr_1.0.2 purrr_0.3.4 readr_1.4.0
[9] tidyr_1.1.2 tibble_3.0.4 ggplot2_3.3.2 tidyverse_1.3.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] Rcpp_1.0.5 lubridate_1.7.9 assertthat_0.2.1 rprojroot_1.3-2
[5] digest_0.6.27 R6_2.4.1 cellranger_1.1.0 backports_1.1.10
[9] reprex_0.3.0 evaluate_0.14 httr_1.4.2 highr_0.8
[13] pillar_1.4.6 rlang_0.4.8 readxl_1.3.1 rstudioapi_0.11
[17] blob_1.2.1 rmarkdown_2.5 labeling_0.4.2 bit_4.0.4
[21] munsell_0.5.0 broom_0.7.2 compiler_4.0.3 httpuv_1.5.4
[25] modelr_0.1.8 xfun_0.18 pkgconfig_2.0.3 htmltools_0.5.0
[29] tidyselect_1.1.0 workflowr_1.6.2 fansi_0.4.1 calibrate_1.7.7
[33] crayon_1.3.4 dbplyr_1.4.4 withr_2.3.0 later_1.1.0.1
[37] MASS_7.3-53 grid_4.0.3 jsonlite_1.7.1 gtable_0.3.0
[41] lifecycle_0.2.0 DBI_1.1.0 git2r_0.27.1 magrittr_1.5
[45] scales_1.1.1 cli_2.1.0 stringi_1.5.3 farver_2.0.3
[49] fs_1.5.0 promises_1.1.1 xml2_1.3.2 ellipsis_0.3.1
[53] generics_0.0.2 vctrs_0.3.4 tools_4.0.3 bit64_4.0.5
[57] glue_1.4.2 hms_0.5.3 yaml_2.2.1 colorspace_1.4-1
[61] rvest_0.3.6 memoise_1.1.0 knitr_1.30 haven_2.3.1 ```````````````````